THIS POST IS UP TO DATE
This post reflects the ENERGY STAR program changes which became effective October 23, 2023.
If you’re considering replacing your home’s windows, you may have some questions about buying energy-efficient windows. It makes sense that you might feel overwhelmed.
Understanding the language and data related to energy efficiency can feel like a challenge to even the savviest, most data-loving homeowners. Our customers who want to buy new windows in the Holly Springs, NC area usually have lots of questions about what all of the energy ratings and certifications mean.
That’s why we wrote this comprehensive, easy-to-understand guide to buying energy-efficient windows.
Why Buying Energy-Efficient Windows Matters
According to the National Fenestration Rating Council, the average American household spends $1,500 – $2,500 on energy costs per year. Around 45% of that cost is for heating and cooling.
So, when buying new windows for your home, it makes sense that you want them to be energy efficient. That way, you can keep your home more comfortable and avoid overspending on energy costs.
The Basics of Buying Energy-Efficient Windows: NFRC Ratings
The National Fenestration* Rating Council (NFRC) is a non-profit organization in the United States. The NFRC maintains an energy efficiency certification and labeling program for windows, windows, and skylights.
*Fenestration refers to all things related to windows, windows, and skylights. It derives from the Latin word “fenestra,” meaning “opening.”
The NFRC provides performance standards for manufacturers’ ratings for these products in five categories:
- U-Factor
- Solar Heat Gain Coefficient
- Visible Transmittance
- Air Leakage
- Condensation Resistance
These ratings serve several purposes.
They help architects, builders, and homeowners compare products in regards to their energy efficiency. They also help builders and home designers ensure that the products they are considering meet local building codes.
NFRC Ratings Stickers on Windows
Window manufacturers are responsible for applying an NFRC Rating sticker to their products.
This sticker is customized to the exact window specifications, taking into account the size of the window, the materials it is made from, the energy efficiency of the glass components, etc. Below is a sample rating sticker provided by the NFRC.
If a product does not have this label, the NFRC has not verified the manufacturer’s claims.
Understanding NFRC Ratings when Shopping for Energy-Efficient Windows
U-factor
U-factor is the rate at which a window allows heat from inside the home to escape outside. The lower the U-factor, the more energy-efficient the window.
U-factor ratings range from 0.10-2.00.
Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC)
Solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) is a measure of heat gain inside your home from the sun.
The lower a window’s SHGC, the less solar heat it allows into your home. A window with a high SHGC rating is more effective at collecting solar heat during the winter.
SHGC ratings range from 0.00-1.00.
Visible Transmittance (VT)
Visible transmittance (VT) refers to the natural light (but not heat) that a window’s glass components allow to enter your home.
The higher the number, the more light will come through the window.
VT ratings range from 0.00-1.00.
Air Leakage
Air Leakage measures the rate of air movement through a window. This measure may also be called infiltration.
Specifically, the measure indicates how many cubic feet of air can pass through a window in sixty seconds. For this rating, it’s assumed that the airflow is a constant 25mph. That number is then divided by the total area of the window to calculate the air leakage rating.
A window with a low air leakage rating is tighter and will let in less air, than a window with a higher air leakage rating.
It’s important to note that the craftsmanship and products used during installation can also impact a window’s air-tightness. The NFRC rating assumes ideal installation conditions. The shoddy installation will, in effect, raise your window’s air leakage rating.
Air leakage ratings range from 0.10 – 0.30.
Condensation Resistance
Condensation resistance indicates the degree to which a window resists condensation buildup. The higher the number, the better a window resists condensation buildup.
Condensation resistance ratings range from 0 – 100.
One Additional Measure of a Window’s Energy Efficiency: Light-to-solar-gain (LSG)
Light-to-solar gain (LSG) is the ratio between the VT and SHGC in a window. This number indicates how efficient a window’s glass is at allowing natural light into your home while preventing solar heat from entering. The higher the number, the more natural light you can expect to get in your home without having heat transfer through the window.
This number is not always provided by manufacturers, but it can be calculated by dividing VT by SHGC.
Light-to-solar-gain calculation: LSG = VT/SHGC
LSG ratings range from 0.00 – 100.
How are the NFRC Rating and ENERGY STAR Rating Related?
Many homeowners have heard of ENERGY STAR ratings.
ENERGY STAR is a program run by the U.S. Department of Energy and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. The program promotes energy efficiency by labeling a wide range of products as meeting ENERGY STAR requirements.
In addition to doors, windows, and skylights, ENERGY STAR rates household appliances, computers, lightbulbs, and more.
A product having an ENERGY STAR certification means that it meets a minimum standard of energy efficiency. An ENERGY STAR certification indicates that a window:
- is manufactured by an ENERGY STAR partner,
- is independently tested, certified, and verified by the National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC), and
- has NFRC ratings that meet strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
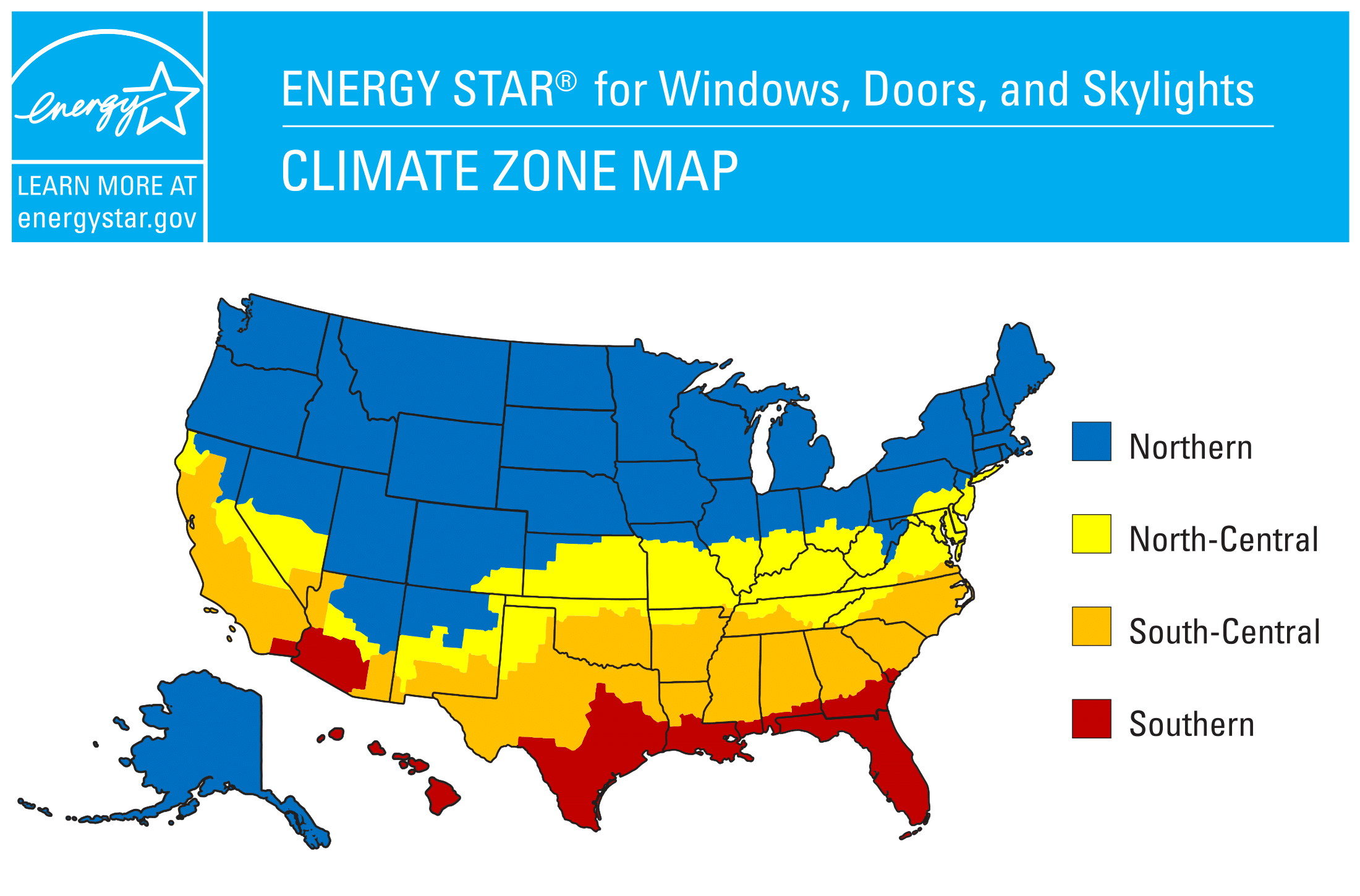
Recommended Window Energy Efficiency Ratings by Climate Zone
Now you understand what the NFRC performance ratings mean in each category.
You also know how these ratings and other factors are used to determine if a product meets ENERGY STAR standards for certification.
But, before you can decide if a window is really energy efficient for your home, you must also know which climate zone you are in to determine which rating criteria your windows should meet.
ENERGY STAR Provides a Climate Zone Map that Splits the United States into Four Climate Zones:
- Northern
- North Central
- South Central
- Southern
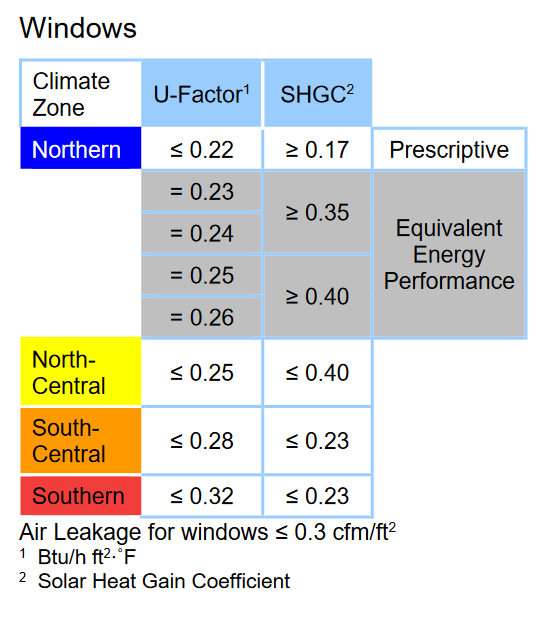
Here in Wake County, North Carolina, we are in the South-Central Climate Zone for ENERGY STAR ratings.*
*Prior to October 23, 2023, Wake County was in the North-Central Climate Zone.
If you happen to be in a different area, you can use this website to search for your state/county and determine which ENERGY STAR climate zone you are in.
In the South-Central climate zone, in order to receive ENERGY STAR certification, windows must meet the following criteria:
Putting it all Together to Find the Best Energy Efficient Windows for your Home
So, now you:
- Know the 5 NFRC ratings, and understand what each measure
- See how NFRC ratings (plus a few other factors) contribute to a window receiving an ENERGY STAR approval. This will also depend on which climate zone you are in.
Armed with this information, you can evaluate the windows you’re considering purchasing. You can be sure that they will not only look great but they will also help you cut back on your home’s energy expenditure.
Expert Window Installation Company Serving Holly Springs, NC, and Surrounding Areas
When you’re looking to replace the windows in your home, you want to make the best choice for your family and your wallet. We hope that this easy-to-read guide will help you do just that.
The Window Works Co. has helped thousands of families in the Raleigh area find the energy-efficient windows they’re looking for.
When you’re ready to replace your old windows with new, energy-efficient windows, we’d love to help you.
Use the calendar below to schedule a window consultation call with us!